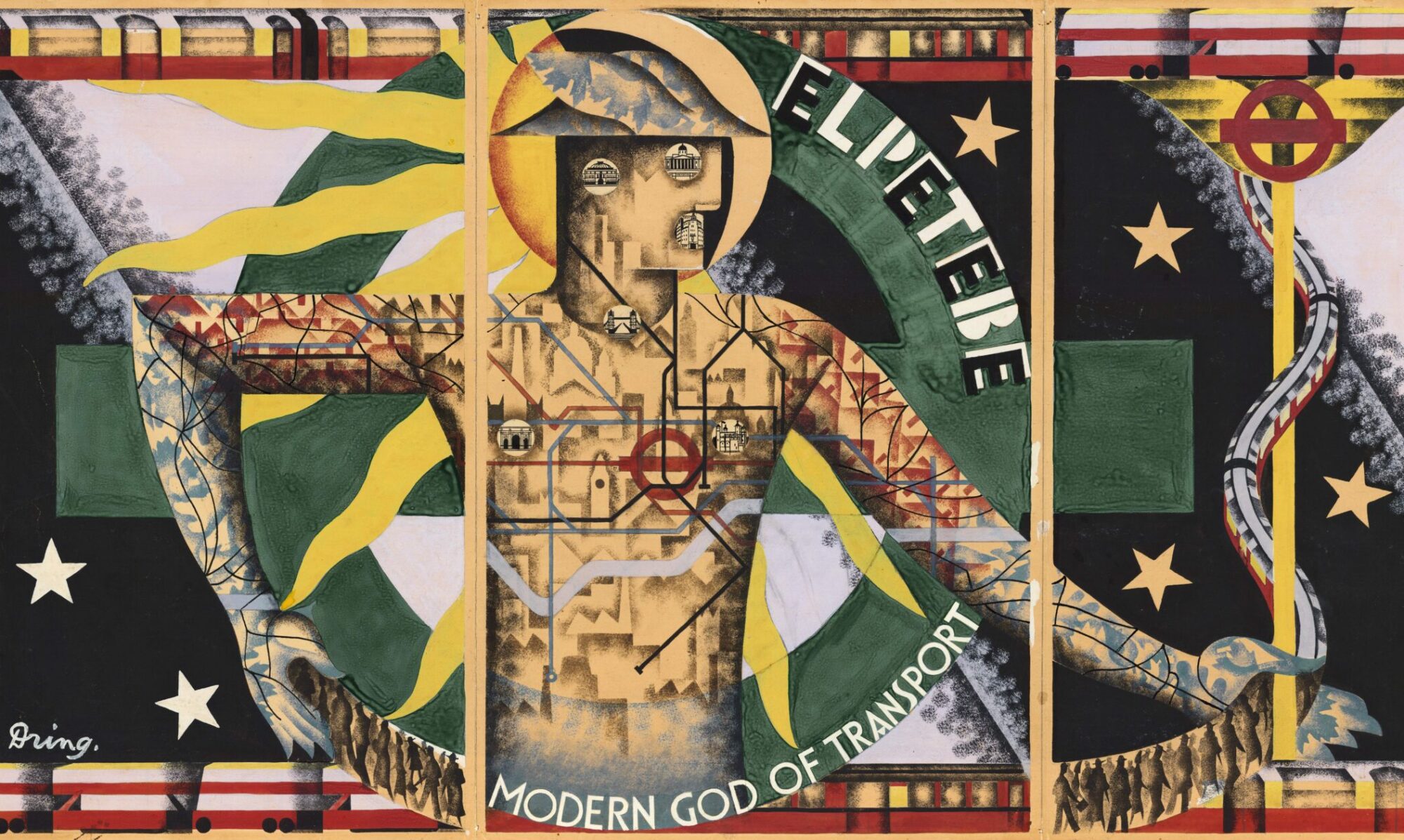
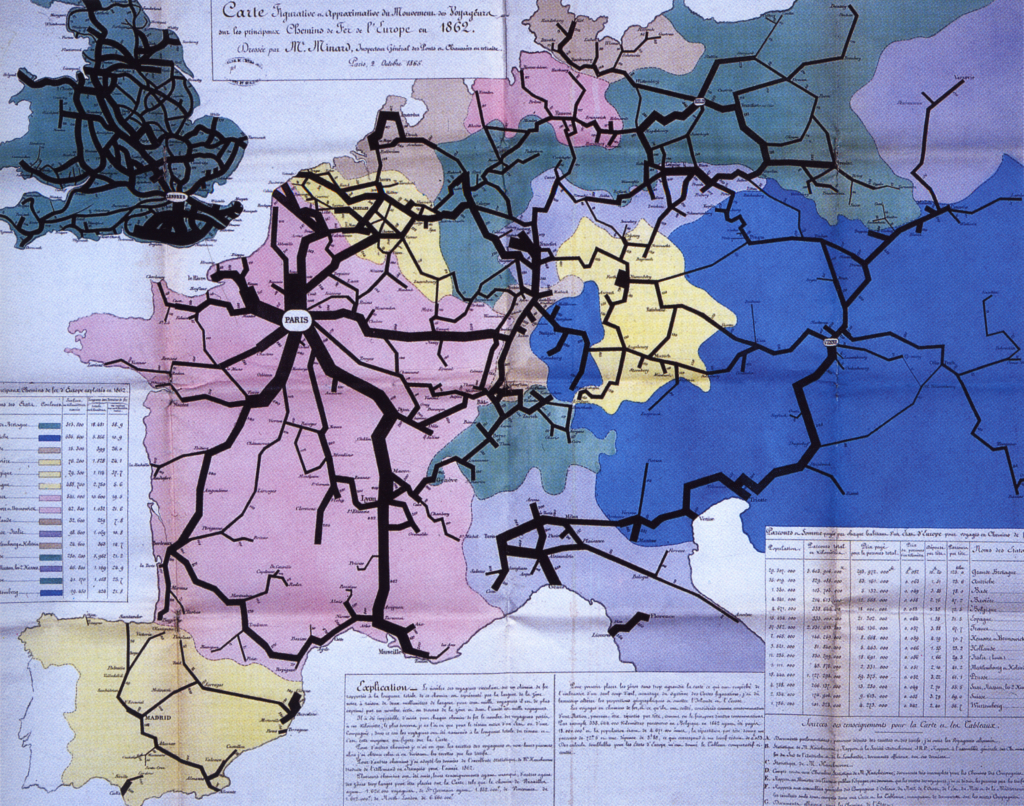
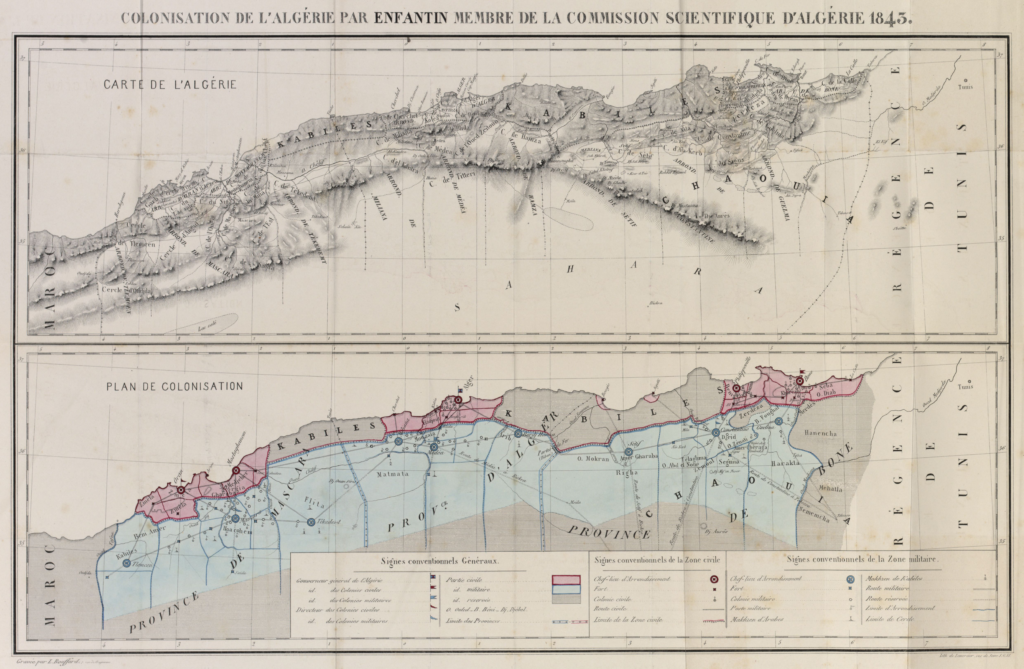
So I continue with another image that represents a significant entry in my network history The Connectivity of Things: Network Cultures since 1832. The book came out on October 15, by the way. Chapter 4 follows the twisted paths of Saint Simonianism. Yet, this week’s image is not as ambivalent as the rest of the chapter which deals with early socialism’s colonial ambitions. Polytechnicien Charles Joseph Minard’s 1862 statistical map of European railroad traffic rather underscores the Saint-Simonian ambitions for a mobilized industrial Europe. Minard’s other statistical maps and diagrams have become a classic in the history of visualizing information. But this image primarily expresses the ambitions of Saint-Simonianism to create a vibrating infrastructural network for the good of society.